Difference between revisions of "SETTINGS/General/Support Material/Support Options/Air Gap"
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
In this example, the distance between the top of the support material and the bottom of the model is 0.2 mm.}} | In this example, the distance between the top of the support material and the bottom of the model is 0.2 mm.}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Here's an animation which will hopefully demonstrate a little better how the air gap works. As you can see, the first layer of the part is lifted up for the air gap, but then for the second layer it moves back down to where it would have been otherwise. In other words, the air gap does not shift the entire object up, only the first layer. This ensures that the first layer is loosely connected to the support, but subsequent layers are printed normally. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Air Gap Animation.gif]] | ||
Revision as of 09:37, 8 April 2016
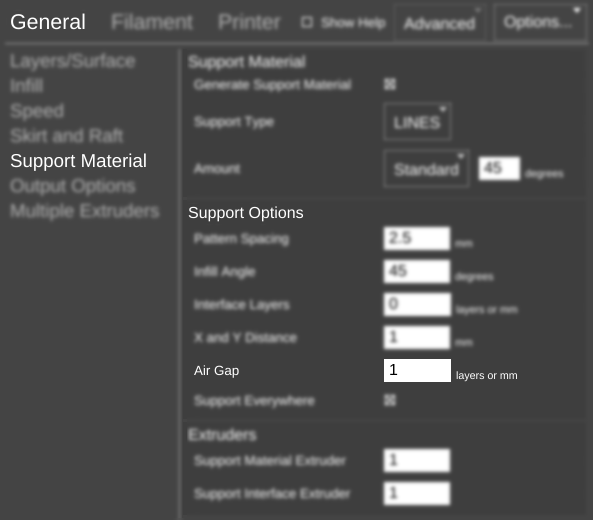
Function
The distance to skip between the support (including interface layers) and the model. For PLA and ABS a value between 0.1 and 0.3 generally works well.
In MatterControl 1.5, Z Gap was changed to Air Gap. Z Gap only worked in increments of the layer height. Air Gap can be any distance.
Parameters
- millimeters (mm)
Can be zero.
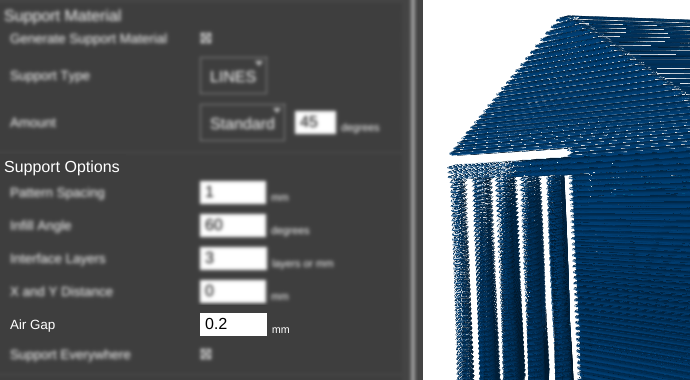
Example(s)
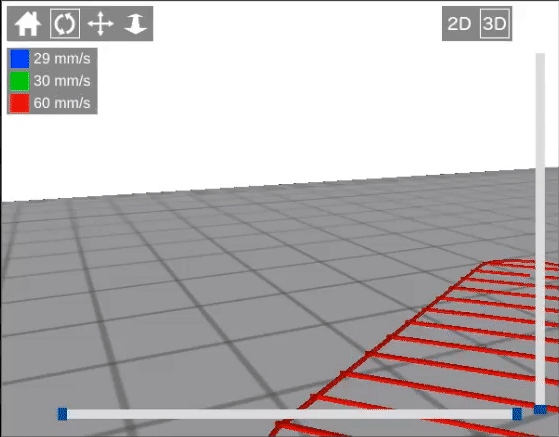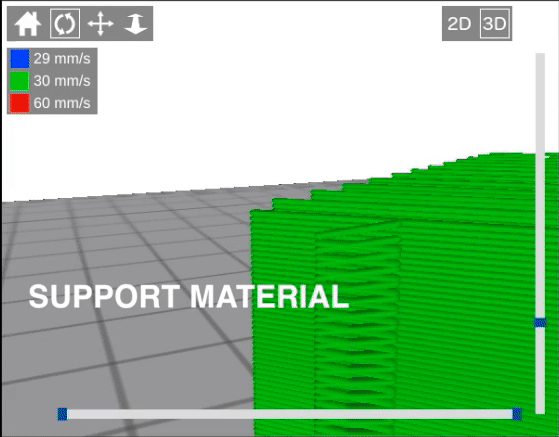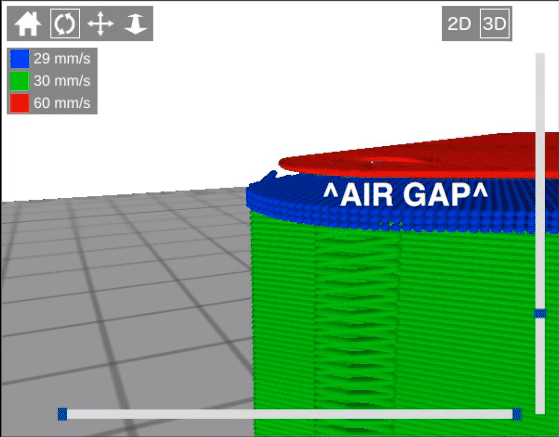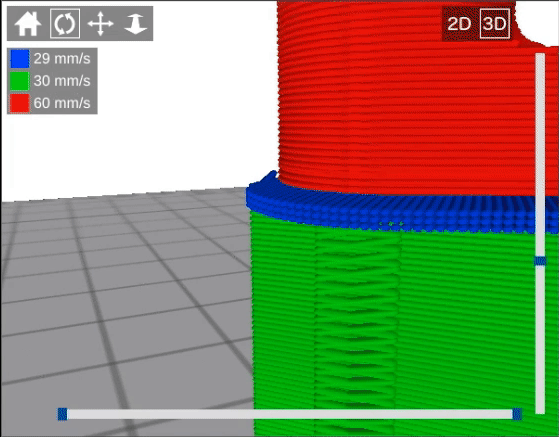
For this example, Support_test.stl is the model used.
mm
In this example, the distance between the top of the support material and the bottom of the model is 0.2 mm.
Here's an animation which will hopefully demonstrate a little better how the air gap works. As you can see, the first layer of the part is lifted up for the air gap, but then for the second layer it moves back down to where it would have been otherwise. In other words, the air gap does not shift the entire object up, only the first layer. This ensures that the first layer is loosely connected to the support, but subsequent layers are printed normally.